Art experimentation is transforming the contemporary art landscape through innovative techniques, alternative materials, and cutting-edge technologies. From bio-art and VR installations to AI-generated compositions and process-based art, artists are pushing creative boundaries and redefining artistic expression. This comprehensive guide explores experimental art practices, key techniques, challenges, and the future of creative experimentation in the art world.
Table of Contents
- What is Art Experimentation?
- The Evolution of Artistic Expression Through Experimentation
- Renaissance Innovation and Scientific Art Experimentation
- Modern Art Movements Born from Experimentation
- Contemporary Alternative Art Media and Experimentation
- Digital Art as a Form of Experimentation
- Immersive Technologies: VR and AR in Art
- Interactive Installations and Audience Participation
- Bio-Art and Living Materials
- Environmental and Land Art Experimentation
- Sound Art and Audio Experimentation
- Top 5 Techniques in Art Experimentation
- Techniques and Approaches in Contemporary Art Experimentation
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration
- Process-Based Art Experimentation
- Chance and Randomness
- Challenges and Considerations
- The Role of Technology in Modern Art Experimentation
- Community and Collaboration
- Educational Approaches
- The Future of Art Experimentation
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions
Art experimentation drives some of the most exciting changes in today’s art world. From virtual reality installations to bio-art, artists are pushing the boundaries of traditional materials, exploring radical new techniques, and redefining what art can be. As contemporary creators continue challenging conventional boundaries through creative experimentation and exploratory art practice, artistic experimentation has become the driving force behind some of our time’s most innovative and thought-provoking works. Through studio experimentation and experimenting with art styles, artists are discovering unprecedented forms of creative experimentation.

What is Art Experimentation?
Art experimentation is the practice of testing new materials, techniques, or ideas in art-making. It challenges traditional practices to create unique, often unexpected forms of creative experimentation and expression. This approach involves stepping beyond established methods through visual experimentation and exploratory art practice to discover novel ways of expressing ideas and creating aesthetic experiences. Whether through contemporary global art trends or pushing artistic extremes, experimenting with art styles has become central to modern artistic experimentation and art exploration.
The Evolution of Artistic Expression Through Experimentation
Art experimentation has always been at the heart of artistic evolution. Throughout history, artists have continuously sought new ways to express their ideas, emotions, and observations about the world around them through experimental art practices. What we consider traditional mediums today—oil painting, marble sculpture, and watercolour—were once revolutionary innovations that challenged the artistic norms of their time.

Renaissance Innovation and Scientific Art Experimentation
The Renaissance period marked a significant era of art experimentation, with masters like Leonardo da Vinci not only perfecting traditional techniques but also inventing new ones. Da Vinci’s scientific approach to art, anatomical studies, and innovative use of sfumato technique demonstrate how artistic experimentation and visual experimentation can lead to breakthrough moments that define artistic movements. This period established the foundation for studio experimentation as a legitimate artistic practice.
Modern Art Movements Born from Experimentation
In the 20th century, movements like Cubism, Surrealism, and Abstract Expressionism emerged from artists’ desire to engage in creative experimentation with form, colour, and concept. Pablo Picasso’s collages introduced everyday materials into fine art, while Jackson Pollock’s action paintings revolutionised art exploration through new approaches to abstract composition and process-based art. These examples show how art experimentation continues to reshape our understanding of artistic possibility, influencing everything from painting genres and styles to modern home decor.

Contemporary Alternative Art Media and Experimentation
Today’s artists have access to an unprecedented array of materials, technologies, and platforms for art experimentation. The digital age has opened doors to entirely new forms of artistic experimentation and art exploration unimaginable decades ago.
1. Digital Art as a Form of Experimentation
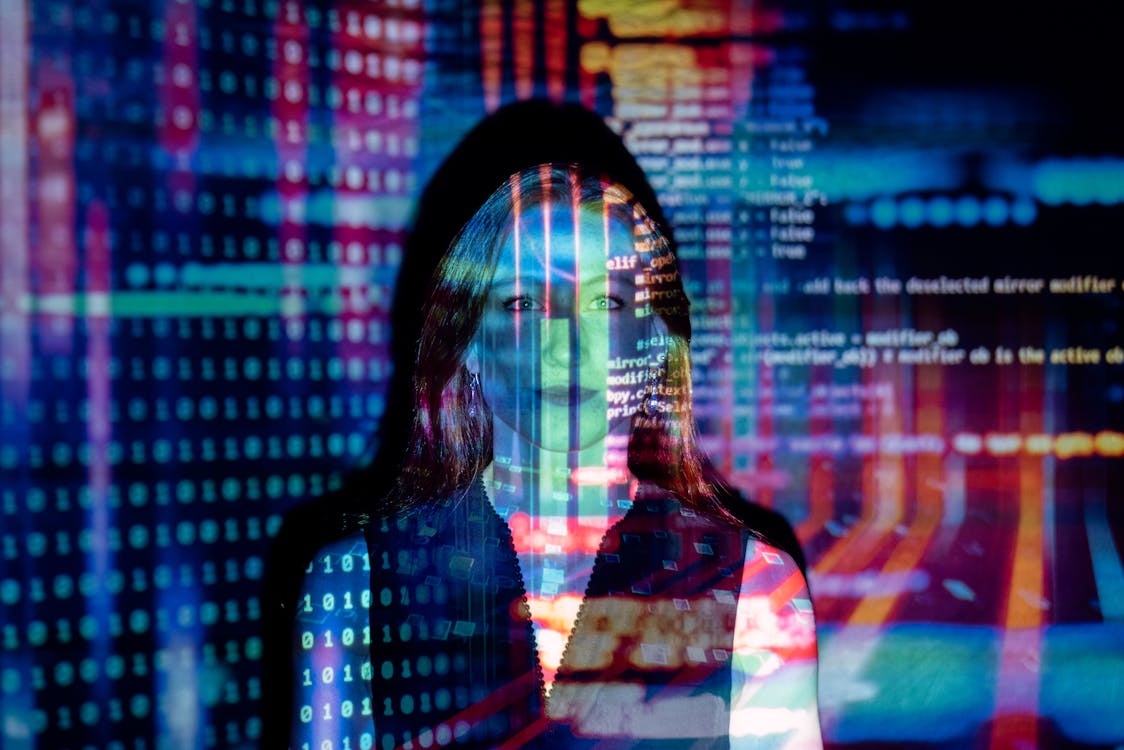
Digital art represents one of the most significant areas of art experimentation in the contemporary art world. Artists use computers, software, and digital tools to create works purely in virtual space or innovatively combine digital and physical elements through visual experimentation and exploratory art practice. This form of creative experimentation has transformed how we think about creative alternative art.
Key characteristics of digital art experimentation:
- Software-based creation: Artists use programmes like Adobe Creative Suite, Processing, and TouchDesigner for visual experimentation
- Generative systems: Algorithms create autonomous artworks through process-based art approaches
- Hybrid approaches: Combining traditional and digital techniques for unique experimentation with art styles
- NFT integration: Blockchain technology creates new markets for digital experimental art practices
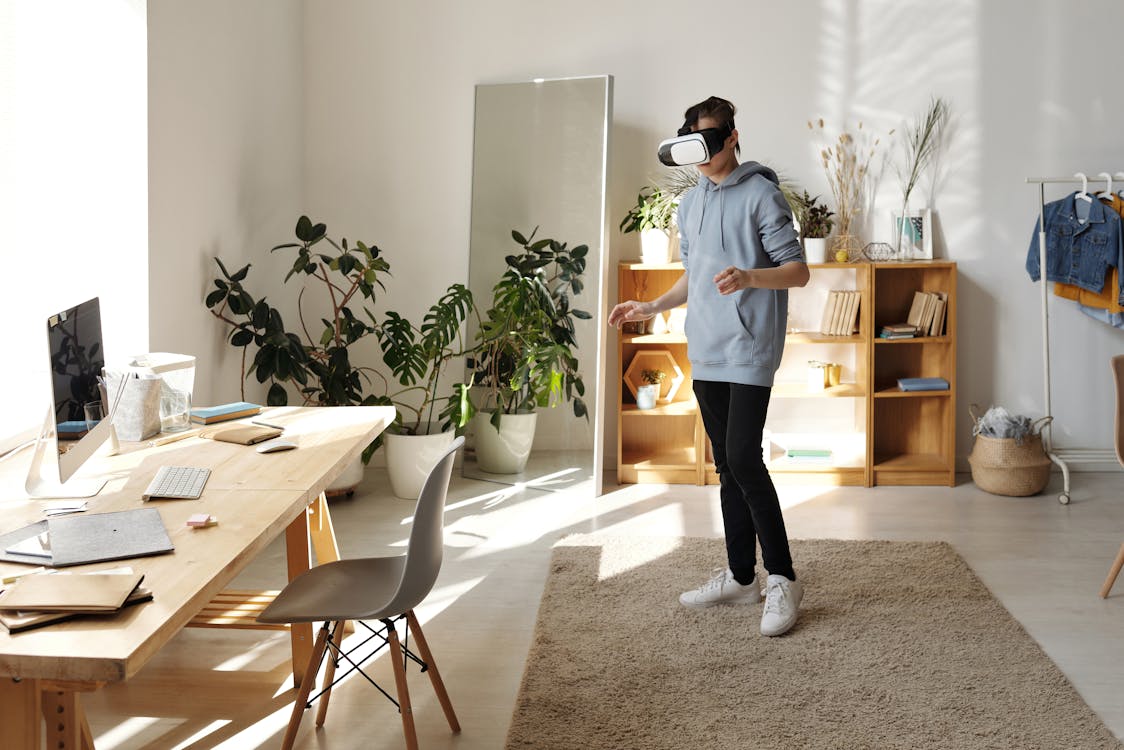
2. Immersive Technologies: VR and AR in Art
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality have become powerful tools for art experimentation, allowing artists to create immersive experiences that transport viewers into entirely new worlds. Artists like Laurie Anderson and Jon Rafman have pioneered VR technology to develop narrative-driven art experiences that blur the lines between storytelling, gaming, and traditional visual art through experimental art practices.
3. Interactive Installations and Audience Participation
Interactive installations represent another frontier in art experimentation, where viewers actively participate in the artistic experience through process-based art. These works often incorporate sensors, cameras, and computer programmes that respond to human movement, touch, or voice, creating dynamic artworks that change based on audience interaction—a perfect example of experimenting with art styles in contemporary practice.
Examples of interactive installation techniques:
- Motion sensors that trigger visual or audio responses in studio experimentation
- Touch-sensitive surfaces that alter the artwork’s appearance through visual experimentation
- Voice-activated elements that respond to audience participation in creative experimentation
- Biometric sensors measuring heart rate or brain activity for exploratory art practice
4. Bio-Art and Living Materials
One of the most controversial and fascinating areas of art experimentation involves using living materials and biological processes. Bio-artists work with bacteria, plants, genetic material, and even living tissue to create artworks that grow, evolve, and decay over time through process-based art and exploratory art practice.
Eduardo Kac’s transgenic art, including his famous “GFP Bunny” project, represents a radical form of artistic experimentation that raises questions about genetic modification, ethics, and the boundaries between art and science. Similarly, artists like Suzanne Anker and Adam Zaretsky work with biological materials to create installations that challenge our understanding of life, death, and transformation through visual experimentation.
This type of art experimentation requires artists to collaborate with scientists, learn laboratory techniques, and grapple with complex ethical questions about manipulating living organisms for artistic purposes. It represents the pinnacle of studio experimentation, meeting scientific inquiry.
5. Environmental and Land Art Experimentation
Environmental art and land art represent forms of art experimentation that work directly with natural materials and landscapes, drawing inspiration from art inspired by nature. Artists like Andy Goldsworthy create temporary sculptures using only natural materials found on-site – stones, leaves, ice, sand – that are documented photographically before returning to nature through process-based art.
Large-scale land art projects like Robert Smithson’s “Spiral Jetty” or Walter De Maria’s “The Lightning Field” demonstrate how creative experimentation can transform entire landscapes into artistic experiences. These works challenge traditional notions of the gallery space and art ownership, as they often exist in remote locations and change over time due to natural processes – exemplifying exploratory art practice at its finest.
6. Sound Art and Audio Experimentation
Sound art represents a rich field for art experimentation that extends beyond traditional music into the realm of pure sonic experience. Artists like Janet Cardiff create sound walks that overlay historical audio onto present-day locations, while composers like John Cage pioneered chance-based composition techniques that challenged conventional musical structures through experimental art practices.
Sound experimentation involves unconventional instruments, found sounds, field recordings, and electronic manipulation through visual experimentation of sonic landscapes. The rise of digital audio workstations and sound processing software has democratised sound art, allowing artists to create complex sonic landscapes without traditional musical training, making studio experimentation more accessible than ever.
Top 5 Techniques in Art Experimentation
Key techniques in creative experimentation include:
- Cross-disciplinary collaboration – Working with scientists, programmers, engineers, and other specialists to push boundaries in artistic experimentation
- Chance-based creation – Using random elements and algorithms to guide artistic decisions in process-based art
- Use of unconventional materials – Incorporating bacteria, data, light, or digital code as artistic mediums through exploratory art practice
- Technology integration – Employing AI, VR, sensors, and advanced fabrication tools for visual experimentation
- Time-based and process-driven approaches – Creating works that evolve, decay, or change over time through experimenting with art styles


Techniques and Approaches in Contemporary Art Experimentation
Successful art experimentation requires both technical skill and conceptual innovation. Artists must master new tools and technologies while developing unique artistic voices that justify their chosen mediums through creative experimentation and mindful artistic practice.
1. Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration in Art Experimentation
Modern art experimentation often requires collaboration between artists and experts from other fields. Digital artists work with programmers, bio-artists collaborate with scientists, and installation artists partner with engineers and fabricators. This collaborative approach reflects the complex nature of contemporary experimental art practices and the specialised knowledge required to work with advanced technologies, similar to how diversity and inclusivity in art bring multiple perspectives together.
Benefits of cross-disciplinary collaboration:
- Access to specialised technical expertise for studio experimentation
- Novel perspectives that challenge conventional approaches in visual experimentation
- Shared resources and equipment for creative experimentation
- Enhanced problem-solving through diverse skill sets in exploratory art practice
2. Process-Based Art Experimentation
Many forms of art experimentation focus on process-based art rather than final products. Process-based art emphasises the act of creation, the development of systems, and the documentation of change over time through exploratory art practice. This approach challenges traditional notions of the art object and questions what constitutes a finished artwork.
Performance art is an extreme form of process-based art and studio experimentation in which the artist’s body and actions become the medium. Artists like Marina Abramović have pushed the boundaries of endurance, vulnerability, and human connection through performances lasting hours, days, or even months—exemplifying artistic experimentation at its most visceral.
3. Chance and Randomness in Art Experimentation
Incorporating chance operations and random elements has been a significant aspect of art experimentation since the mid-20th century. From John Cage’s I Ching-based compositions to contemporary artists using computer algorithms to generate visual art, randomness can introduce unexpected elements that push creative experimentation in new directions.
Generative art, created through autonomous systems and algorithms, represents a contemporary form of art experimentation that explores the relationship between human creativity and machine processes through visual experimentation. Artists programme systems that create artworks independently, raising questions about authorship, creativity, and the artist’s role in the creative process—a fascinating exploration of experimenting with art styles in the digital age.
Challenges and Considerations in Art Experimentation
Art experimentation with alternative media has unique challenges that artists must navigate carefully through thoughtful exploratory art practice.
1. Technical Complexity
Experimenting with new technologies or unconventional materials often demands skills that go beyond traditional studio training. Artists must invest time learning new skills, understanding equipment limitations, and troubleshooting technical problems. This technical complexity can sometimes overshadow conceptual development, leading to works that are technically impressive but conceptually weak—a risk in any experimental art practices.

Common technical challenges include:
- Steep learning curves for new software and hardware in visual experimentation
- Equipment failures and technical malfunctions during creative experimentation
- Limited access to specialised tools and facilities for artistic experimentation
- Rapidly evolving technology requires constant skill updates in studio experimentation
2. Preservation and Documentation
Many forms of art experimentation create works that are ephemeral, interactive, or dependent on specific technologies. Preserving these works for future generations presents significant challenges for museums, collectors, and art historians. Time-based media, software-dependent works, and biological art require specialised preservation strategies, much like antique picture framing requires specific conservation approaches. Understanding art framing in interior design can help with proper preservation.
3. Ethical Considerations
Some experimental practices-particularly bio-art and works involving living organisms-raise complex ethical questions that artists must carefully consider.Artists must consider the welfare of living organisms, the implications of genetic modification, and the potential societal impacts of their work. These moral considerations require careful thought and often consultation with ethicists and scientific review boards.
4. Market and Institutional Support
The art market and traditional art institutions sometimes struggle to accommodate experimental art practices. Works that can’t be easily collected, displayed, or sold face challenges in finding support and audiences. However, alternative spaces, online platforms, and new funding models are emerging to support art experimentation. Understanding creative painting display ideas and art lighting tips can help experimental works find their place in traditional and contemporary spaces.
The Role of Technology in Modern Art Experimentation
Technology has become an indispensable tool for art experimentation in the 21st century. From simple digital tools to complex artificial intelligence systems, technology offers artists new ways to create, manipulate, and present their work through creative experimentation and visual experimentation.

1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning represent the cutting edge of art experimentation in the digital realm. Artists are training neural networks on artistic datasets, creating algorithms to generate novel visual compositions, and exploring the creative potential of machine intelligence through experimental art practices.
Projects like Google’s DeepDream, which uses neural networks to generate surreal imagery, have inspired artists to explore the aesthetic possibilities of machine vision. Artists like Mario Klingemann and Helena Sarin have developed sophisticated AI systems that create artworks independently.These practices challenge long-held ideas about authorship, creativity, and the role of the artist in an age of intelligent systems.
AI applications in art experimentation:
- Neural style transfer for unique visual experimentation
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs) create original imagery through process-based art
- Text-to-image generation for creative experimentation
- Machine learning pattern recognition in exploratory art practice
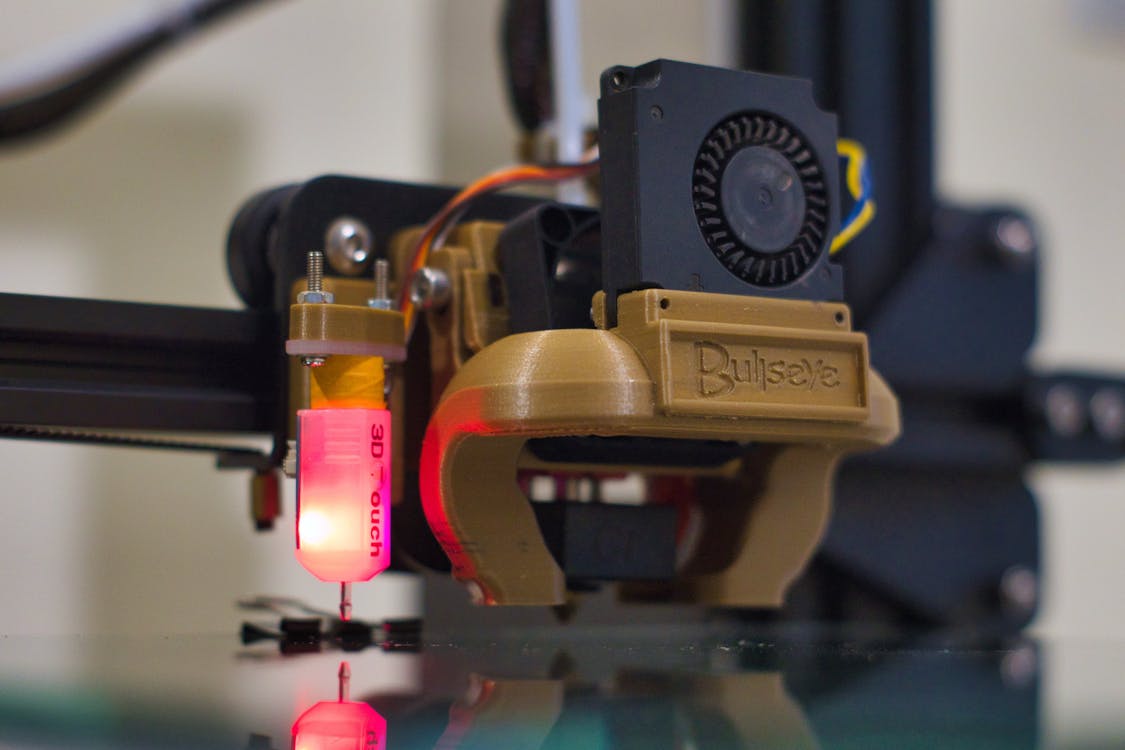
2. 3D Printing and Digital Fabrication
Digital fabrication technologies have revolutionised art experimentation by allowing artists to create complex three-dimensional forms that would be impossible to produce by hand. 3D printing, laser cutting, and CNC milling enable artists to translate digital designs into physical objects with precision and repeatability through studio experimentation.
This technology has been particularly transformative for sculptors and designers who can now create intricate geometries, impossible structures, and customised forms through exploratory art practice. Artists like Joshua Harker and Bathsheba Grossman have pushed the boundaries of what’s possible with 3D printing, creating sculptures at the intersection of art, mathematics, and engineering—perfect examples of experimenting with art styles through technology.
3. Virtual and Augmented Reality in Art Experimentation
VR and AR technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for art experimentation by creating entirely new spaces for artistic experience. These technologies allow artists to construct virtual worlds, overlay digital information onto physical spaces, and create immersive narratives that engage multiple senses through process-based art and visual experimentation.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated interest in virtual art spaces, with museums and galleries creating online exhibitions and artists developing VR experiences for remote audiences. This shift has highlighted the potential of digital technologies to make art more accessible while opening new avenues for art experimentation and creative experimentation.

Community and Collaboration in Art Experimentation
Art experimentation increasingly takes place within communities of practice that share knowledge, resources, and technical expertise through exploratory art practice. Maker spaces, fab labs, and artist collectives provide infrastructure and support for experimental art practices that individual artists might find impossible to pursue independently, similar to how traditional crafts rely on community knowledge sharing.
Online communities and open-source software have democratised access to tools and knowledge, allowing artists worldwide to participate in art experimentation regardless of their geographic location or institutional affiliation. Platforms like GitHub, where artists share code and collaborate on digital projects, exemplify how art experimentation has become increasingly collaborative and networked.
Key community resources for art experimentation:
- Maker spaces and fab labs offering studio experimentation facilities
- Online forums and Discord servers for creative experimentation discussions
- Open-source software communities supporting visual experimentation
- Artist residencies fostering exploratory art practice
Educational Approaches to Art Experimentation
Art schools and educational institutions are adapting curricula to support art experimentation across disciplines through studio experimentation. Cross-disciplinary programmes that combine art with science, technology, and other fields are becoming more common, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of contemporary experimental art practices and artistic experimentation.
Residency programmes at institutions like MIT’s Centre for Art, Science & Technology and the Eyebeam Art + Technology Centre provide artists access to advanced facilities and expert collaborators, fostering art experimentation that might not be possible in traditional studio settings. These programmes support creative experimentation and exploratory art practice at the highest levels.
The Future of Art Experimentation
As we look toward the future, art experimentation will become even more diverse and technologically sophisticated through continued visual experimentation and experimentation with art styles. Emerging technologies like quantum computing, advanced materials science, and biotechnology will create new possibilities for artistic expression through experimental art practices.
Climate change and environmental concerns are also shaping art experimentation, with artists increasingly focusing on sustainable materials and practices. This ecological consciousness drives innovation in bio-based materials, renewable energy systems for art installations, and artworks that actively contribute to environmental restoration—connecting to themes explored in art inspired by nature.
Future trends in art experimentation:
- Sustainable and eco-friendly practices integrating environmental consciousness into studio experimentation
- Brain-computer interfaces enabling direct neural control of artworks through creative experimentation
- Quantum computing applications for unprecedented computational visual experimentation
- Advanced biomaterials are creating living, responsive artworks through process-based art
- Decentralised platforms democratising access to exploratory art practice
Art experimentation will continue challenging our understanding of what art can be and do through creative experimentation and process-based art. As the boundaries between art, science, technology, and daily life continue to blur, artists will find new ways to engage with pressing social, political, and environmental issues through exploratory art practice. The influence extends even to street art and community-based practices.
Key Takeaways
- Art experimentation encompasses visual experimentation, process-based art, and exploratory art practice across multiple disciplines.
- Creative experimentation and experimental art practices drive innovation in contemporary art through technology, collaboration, and unconventional materials.
- Artistic experimentation challenges traditional boundaries and creates new possibilities for expression through studio experimentation.
- Experimenting with art styles requires balancing technical mastery with conceptual depth and ethical considerations.
- The future of art exploration lies in sustainable practices, emerging technologies, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Understanding how experimental works can be presented through colour psychology, lighting, and balancing paintings with interior design helps make experimental art more accessible and engaging in everyday spaces.
- Regional art scenes, like in Leeds, demonstrate how experimental art practices flourish in diverse communities.
- Technology serves as both a tool and a medium for contemporary art experimentation.
- Collaboration across disciplines enriches artistic experimentation and expands creative possibilities.
- Process-based art emphasises the journey of creation as much as the outcome.
Conclusion
Art experimentation represents the vital, evolving edge of contemporary artistic practice through creative experimentation, visual experimentation, and process-based art. By embracing alternative media, new technologies, and unconventional approaches through exploratory art practice, artists continue to expand the possibilities of artistic experimentation and challenge audiences to see the world in new ways.
The future of art experimentation lies not just in technological advancement but in the thoughtful integration of new tools with meaningful concepts and human experience through studio experimentation and experimenting with art styles. As artists continue to push creative boundaries through experimental art practices, they remind us that art’s most significant power lies in its ability to imagine new realities and inspire us to think differently about our world.
Whether working with cutting-edge technology or ancient materials in new ways, contemporary artists engaged in art experimentation and art exploration are writing the following chapters in art’s long history of innovation and discovery. Their work ensures that art remains a vital, dynamic force for creativity and critical thinking—extending from large-scale paintings to innovative kitchen wall art, and from cultural heritage representation to creating visual depth in small spaces.
Understanding how to display and present experimental works-through framing considerations, room colour schemes, matching paintings with room decor, and artwork and furniture pairing-ensures that creative experimentation reaches wider audiences. As trends in interior decor continue to evolve, experimental works—from large-scale paintings to enhancing interiors with wall art-demonstrate how art can meaningfully transform everyday spaces.
FAQs
Art experimentation involves exploring new techniques, materials, concepts, and approaches to artistic experimentation and creation. It consists of stepping beyond traditional or established methods through visual experimentation and exploratory art practice to discover novel ways of expressing ideas and creating aesthetic experiences. Art experimentation can include anything from trying unconventional materials like bacteria or computer code to developing new techniques for applying traditional materials through studio experimentation and creative experimentation.
An art experience, or experiential art, refers to artworks designed to provide immersive, participatory experiences rather than passive observation through process-based art. These works often involve art experimentation with interactive technologies, environmental installations, or performances that engage multiple senses and invite audience participation through experimental art practices. Examples include virtual reality art installations, interactive digital sculptures, and site-specific works that respond to their environment through experimenting with art styles.
Experimenting in art means actively testing new ideas, techniques, materials, or concepts without being sure of the outcome through creative experimentation and exploratory art practice. Art experimentation involves a willingness to fail, learn from mistakes, and iterate on ideas through studio experimentation. It can mean combining unlikely materials, using familiar materials unexpectedly, or applying techniques from other disciplines to artistic experimentation. The experimental process through visual experimentation is often as necessary as the final result in process-based art.
Examples of experimental art span many media and approaches through art experimentation:
- Bio-art: Eduardo Kac’s genetically modified fluorescent rabbit
- Digital art: Casey Reas’s software-generated visual compositions through visual experimentation
- Sound art: Janet Cardiff’s audio walks and sound installations
- Land art: Andy Goldsworthy’s temporary natural sculptures through process-based art
- Interactive installations: Rafael Lozano-Hemmer’s pulse-responsive environments
- AI art: Mario Klingemann’s neural network-generated portraits through creative experimentation
- Performance art: Marina Abramović’s endurance-based performances
- Video art: Bill Viola’s slow-motion video installations
Each represents art experimentation that has pushed the boundaries of traditional artistic experimentation through exploratory art practice.
Art experimentation techniques include various experimental art practices:
- Cross-disciplinary collaboration: Working with scientists, programmers, or engineers for creative experimentation
- Material exploration: Testing unconventional materials like bacteria, data, or light through visual experimentation
- Process documentation: Recording and analysing creative processes in studio experimentation
- Chance operations: Using random elements to guide creative decisions in process-based art
- Technology integration: Incorporating digital tools, sensors, or AI systems
- Site-specific creation: Making work that responds to particular locations through exploratory art practice
- Time-based approaches: Creating works that change over time
- Audience interaction: Designing works that require viewer participation through experimenting with art styles
Experimental art forms that involve significant art experimentation include:
- Digital and new media art: VR experiences, interactive installations, generative art through visual experimentation
- Bio-art: Working with living materials and biological processes through process-based art
- Sound art: Sonic sculptures, audio environments, experimental music
- Performance art: Live, time-based works using the artist’s body or actions in studio experimentation
- Land art: Large-scale works created in natural environments through exploratory art practice
- Conceptual art: Idea-based works that prioritise concept over traditional craft
- Video art: Moving image works that explore the medium’s unique properties through creative experimentation
Installation art: Three-dimensional environments that transform spaces through artistic experimentation
Abstract art is a fundamental form of experimentation that emerged in the early 20th century through creative experimentation. Artists like Wassily Kandinsky and Piet Mondrian experimented with pure form, colour, and composition through visual experimentation, moving away from representational imagery. Modern abstract art continues this tradition of art experimentation by exploring new materials, techniques, and concepts while focusing on formal elements rather than recognisable subjects through process-based art and experimenting with art styles.
Chance operations have been crucial to art experimentation since artists like John Cage began using I Ching hexagrams to make compositional decisions through experimental art practices. Incorporating randomness through creative experimentation can lead to unexpected discoveries, break habitual patterns, and introduce elements that the artist might not have consciously considered in their studio experimentation. Contemporary art experimentation with AI and generative systems continues this tradition of using chance as a creative tool through exploratory art practice and visual experimentation.
Contemporary art has embraced experimentation as a core principle, with artists regularly working across multiple disciplines and media through experimental art practices. The modern art world values innovation, concept, and pushing boundaries through artistic experimentation over traditional technical skill alone. This has led to the acceptance of video, installation, performance, and digital art as legitimate artistic practices, all of which emerged from art experimentation, creative experimentation, and process-based art approaches.
Technology has become integral to art experimentation in the 21st century through visual experimentation and studio experimentation. Digital tools allow artists to create works impossible with traditional materials through creative experimentation, while technologies like AI, VR, and biotechnology open entirely new creative possibilities for exploratory art practice. However, successful art experimentation with technology requires balancing technical innovation with meaningful artistic content and human experience through thoughtful artistic experimentation and experimenting with art styles.
About the Author
John Sewell
John Sewell is the founder of Cosimo and holds a Master’s Degree in History of Art from the University of Birmingham. He built Cosimo to give emerging artists fair, transparent ways to reach collectors directly. He was also shortlisted for the Great British Entrepreneur Awards. His background in art, creative entrepreneurship and digital marketplaces informs his writing on artist development, accessible art, and the future of online art sales.
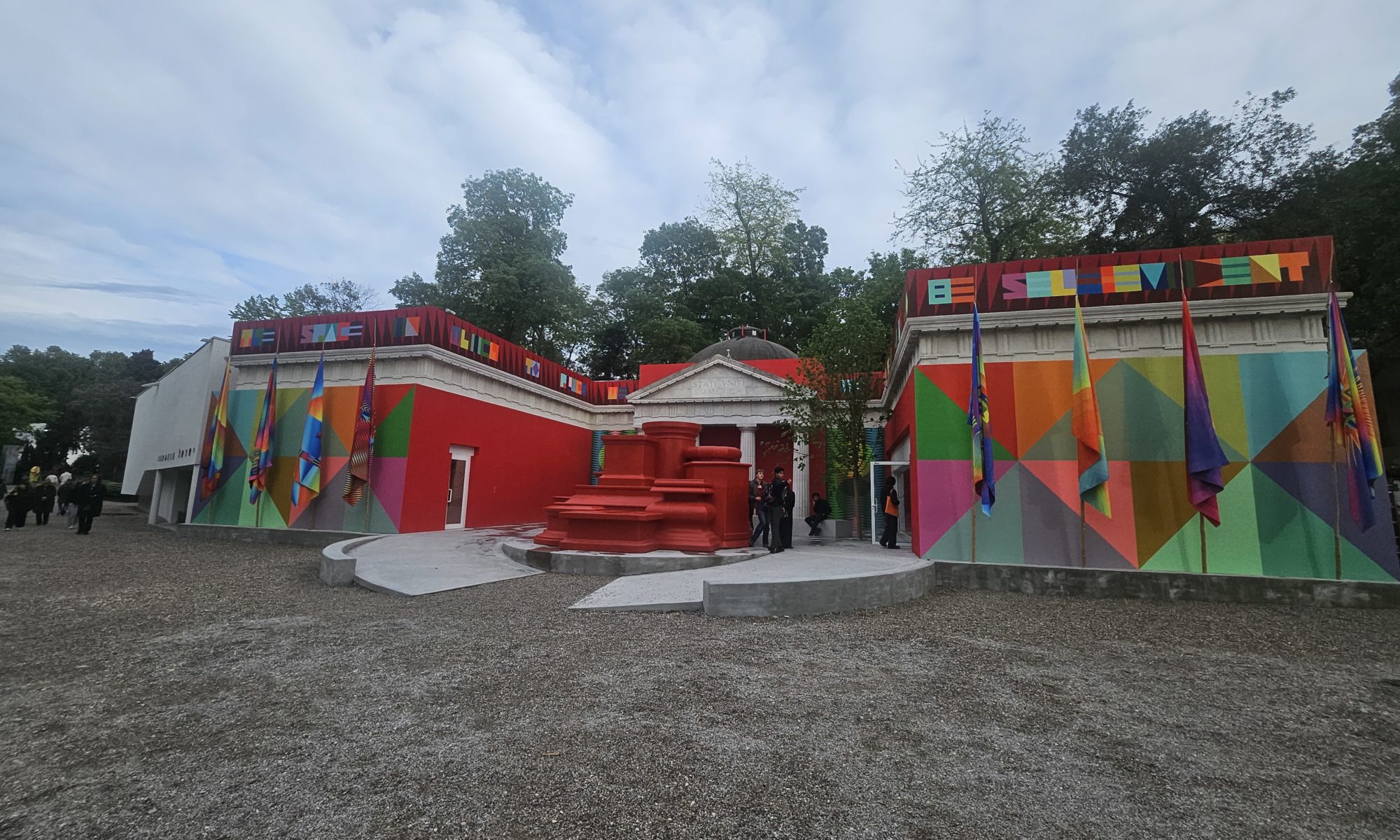




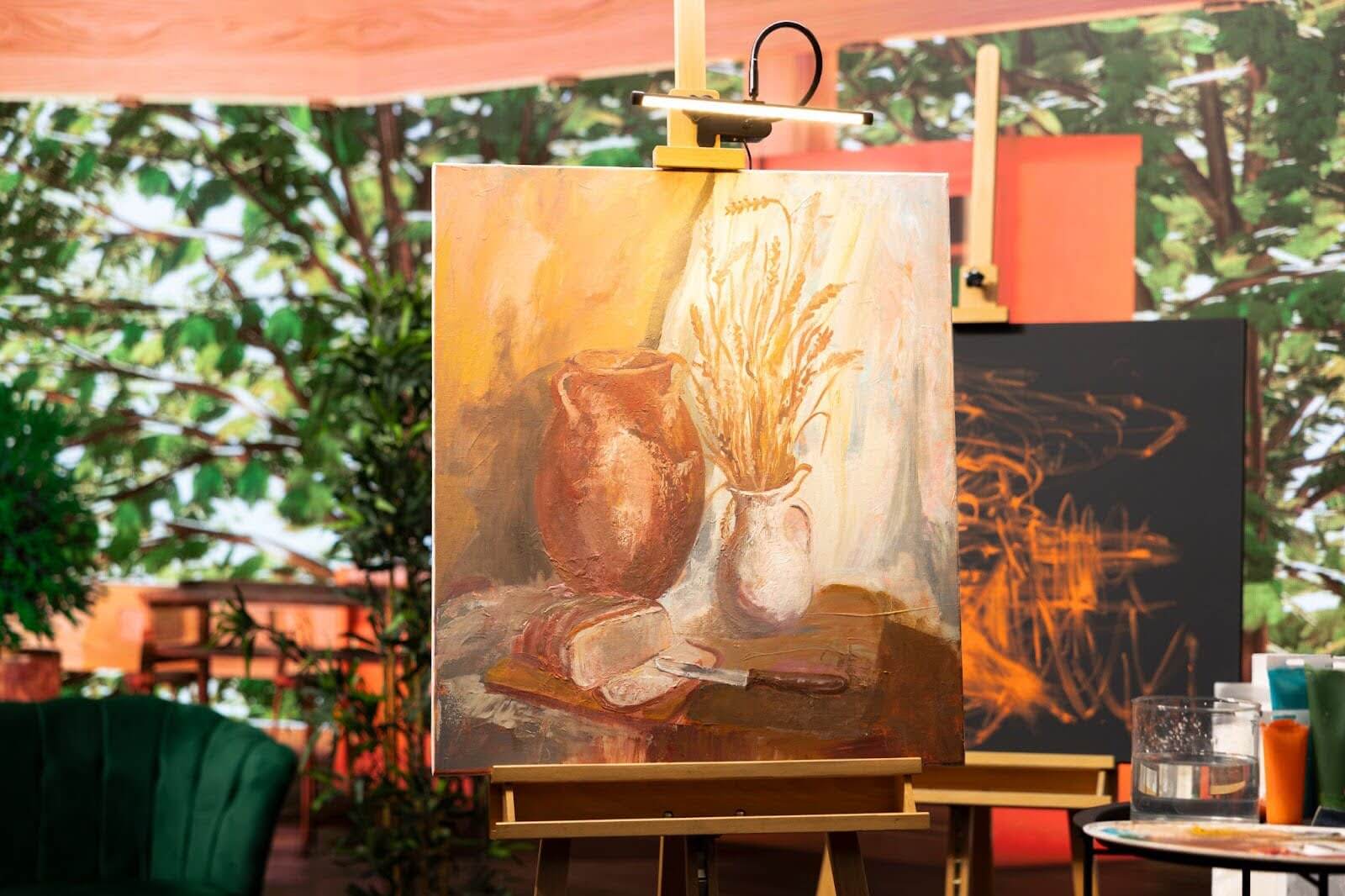




































































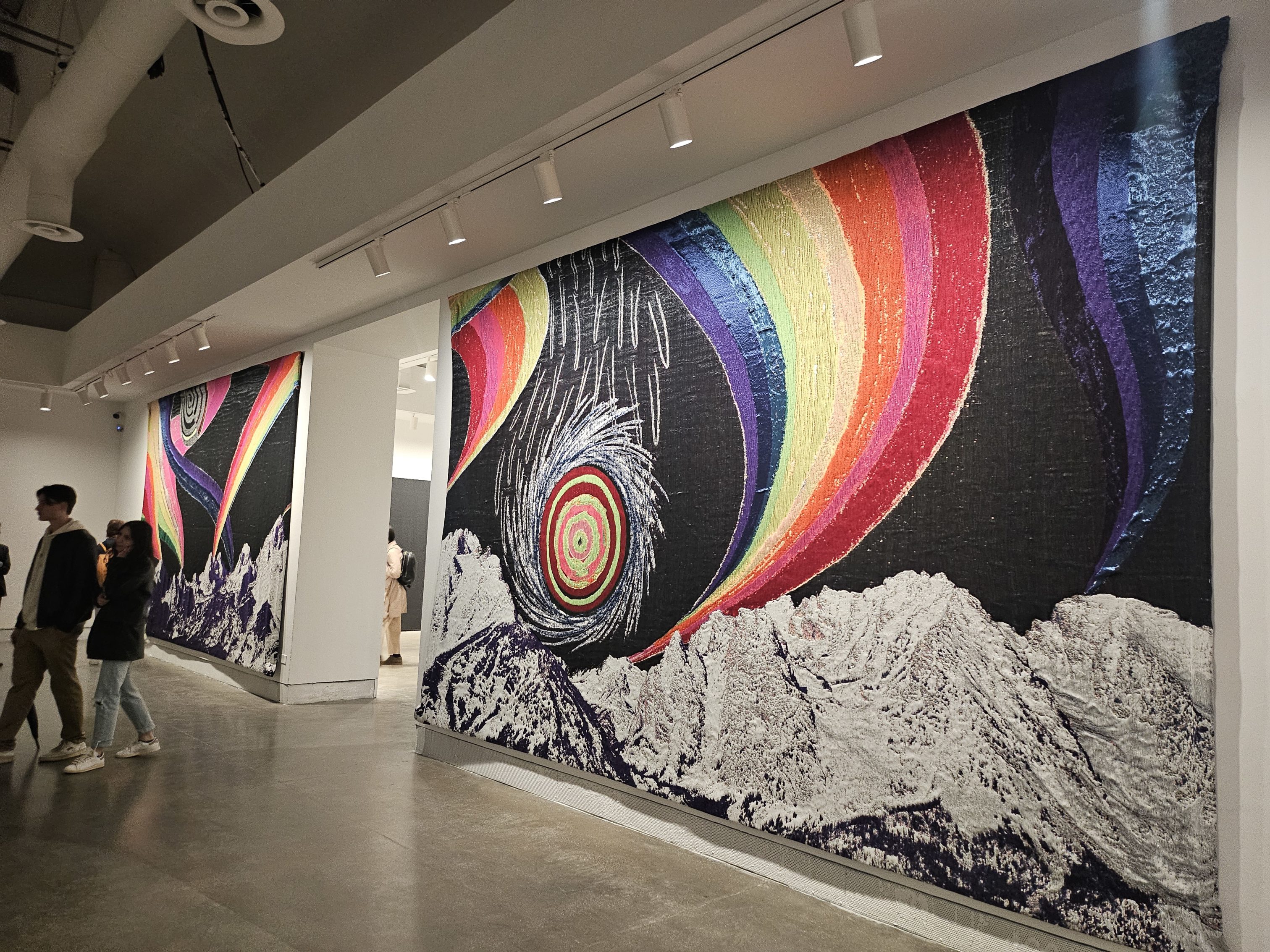
 Location: Belgium Pavilion, Biennale di Venezia 2024
Location: Belgium Pavilion, Biennale di Venezia 2024 


















