Sustainability in Art is becoming increasingly important, especially as more artists turn their creative practices into a reflection of their values. Eco art blends imagination with environmental awareness, showing how recycled materials, non-toxic paints, and mindful techniques can protect the planet while still delivering powerful expression.
In this blog, we delve into the significance of sustainability in art and explore why incorporating eco-friendly elements is of substantial importance to artists in 2026.
Sustainability in Art by Incorporating Sustainable Materials
Artists today are redefining creativity by embracing sustainable materials and methods in their work. Let’s look at how they make a difference by incorporating eco-friendly practices.

A. Artists Utilising Recycled and Upcycled Materials in 2026
Recycled materials encompass items processed and transformed back into raw materials for reuse. In contrast, upcycled materials involve a creative renaissance, breathing new life into discarded items and elevating them into products of higher value or quality. The distinction lies in the transformation process: recycling breaks materials into their essential components while upcycling refines existing materials, crafting something entirely new.
Many artists embrace sustainability by ingeniously repurposing materials that have fulfilled their initial purpose. Through innovative thinking, these artists breathe new life into discarded items such as cardboard, bottles, and fabrics, transcending their original utility to craft visually striking and conceptually rich art pieces. This practice not only showcases the boundless nature of creativity but also serves as a tangible example of how reimagining the use of everyday materials can contribute to a more sustainable and eco-conscious artistic landscape.

B. Use of Eco-Friendly Pigments, Inks, and Paints
In the vibrant world of colours, artists are making environmentally conscious choices by selecting paints and inks crafted from pigments derived from natural sources or non-toxic materials. These materials, mindful of the environment, often originate from natural sources such as botanical extracts, minerals, or certain insects, providing sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical-laden options. By embracing pigments made from plant-based sources or other sustainable alternatives, artists actively contribute to reducing harmful chemicals and promoting a healthier environment.
C. Embracing Sustainable Canvases and Papers
Artists are changing the canvas they paint on and the paper they draw on. Some use materials that come from responsibly managed forests or recycled paper. Others might paint on surfaces like reclaimed wood. This way, they support sustainable resources and show how art can be made without harming the Earth.
Artists’ efforts to use recycled materials, eco-friendly pigments, and sustainable canvases highlight a new way of making art that considers the planet and expresses creativity.

Sustainability in Art: Environmental Awareness in 2026
Art has a powerful voice, and today, many artists are using their creativity to raise awareness about sustainability. Let’s explore how art is becoming a messenger for environmental consciousness.

Art Movements Promoting Sustainability and Environmental Consciousness
Art movements advocating sustainability and environmental consciousness are pivotal in shaping a more responsible artistic landscape. One notable movement is Eco-Art, which emerged in the late 20th century. This movement encourages artists to explore ecological issues and promote environmental sustainability through their work. Artists associated with Eco-Art often use recycled materials, address climate change, and engage with nature in their creations.
Another impactful movement is Land Art, where artists integrate natural elements into their works, often in outdoor landscapes. This allows the environment to become both the canvas and the source of inspiration for artistic expression. Artists usually arrange, sculpt, or otherwise manipulate elements such as rocks, soil, wood, or vegetation to create their artworks harmoniously with nature. The resulting pieces are often temporary, evolving with the natural elements and changing over time. This movement seeks to connect art and the environment, emphasising the interdependence of artistic expression and the natural world. Artists like Andy Goldsworthy and Robert Smithson have left a lasting mark on the movement, using natural materials to create temporary or permanent installations that interact with their surroundings.
These movements inspire change within the artistic community and draw attention to art’s profound impact in fostering environmental awareness. Through their innovative approaches, artists within these movements contribute to a broader cultural shift, emphasising the potential of art as a catalyst for positive change in our relationship with nature.
Impactful Eco-Conscious Installations and Sculptures
Numerous artists are leaving a lasting impact by crafting large-scale, captivating installations and sculptures that prompt contemplation about one’s relationship with nature. One noteworthy example is German artist HA Schult’s “Trash People” installation. Comprising life-sized human figures made entirely from recycled materials, this piece is a powerful visual commentary on the global issue of waste and consumption.

Additionally, sculptures like the “Breathing Pavilion” by artist and architect Michael Jantzen showcase a fusion of art and sustainable design. This innovative installation responds to environmental conditions, expanding and contracting in response to changes in air quality, symbolising the interconnectedness between human activities and the environment.

Exploring the Narrative of Climate Change and Conservation in Art
Narratives surrounding climate change and conservation are gaining prominence in art. Artists leverage their craft to convey urgent messages about the environment. One such approach is visual storytelling, where artists create pieces that narrate the impacts of climate change and the imperative need for conservation efforts.
A notable example is the work of Xavier Cortada, whose art often centres around environmental issues, specifically climate change. Cortada’s “Underwater HOA” project, for instance, involves the creation of art installations at different elevations to visualise the potential rise of sea levels due to climate change. Through such pieces, artists engage viewers in a powerful dialogue about the Earth’s vulnerability and our collective responsibility to protect it.
Furthermore, artists like Zaria Forman employ hyper-realistic drawings to depict the beauty of our planet, with a focus on endangered environments. Through the intricate details of her work, Forman captures the essence of places affected by climate change, acting as a visual advocate for conservation.
These artists use their creativity to showcase the beauty of the Earth and evoke a sense of responsibility in viewers. The narrative they construct through their art is a compelling call to action, encouraging individuals to consider their role in preserving the planet for future generations. In this way, art becomes a powerful medium for education, provoking thought and inspiring change.

Sustainability in Art by Initiatives and Collaborations
In art, collective effort and innovative initiatives are forging the path towards a more sustainable future.
1. Organisations and Platforms Supporting Sustainable Art Practices in 2026
Numerous organisations and platforms actively champion sustainable art practices, supporting artists committed to environmental responsibility. One exemplary platform is the Sustainable Arts Foundation, which focuses explicitly on supporting artists with families. Through grants and resources, this foundation assists artists in realising projects that align with sustainability principles while addressing the unique challenges of balancing artistic pursuits and family life.

Artist-in-residence programs offer creators the vital space and time for creative exploration, often unfolding in environments prioritising ecological conservation. In these settings, artists can delve into sustainable practices, experiment with eco-friendly materials, and seamlessly integrate these considerations into their artistic process. This dedicated focus aligns with a broader environmental ethos, fostering an environment where artists contribute actively to a more eco-conscious artistic landscape. Through this immersive approach, artist-in-residence programs become catalysts for nurturing creativity and environmental responsibility.
Another impactful organisation is the Center for Sustainable Practice in the Arts (CSPA), dedicated to integrating sustainability into the creative process. CSPA facilitates dialogues, offers resources, and recognises sustainable practices within the arts community. Their initiatives range from promoting eco-friendly production methods to fostering a broader understanding of sustainability in artistic endeavours.
These platforms are pivotal in fostering a community that values and encourages sustainable art. By offering financial support, resources, and exhibition opportunities, they empower artists to create impactful work and contribute to a broader conversation on the intersection of art and environmental responsibility.
2. Collaborative Projects Focusing on Environmental Issues
Artists often team up to work on projects centred around environmental concerns. These collaborations produce impactful pieces illuminating climate change, pollution, or biodiversity loss. Through joint efforts, artists convey powerful messages, aiming to inspire action and awareness in the community.

Emerging Sustainable Art Practices in 2026
As we progress through 2026, new sustainable practices are transforming the art world:
1. Digital and NFT Sustainability
Artists are increasingly adopting energy-efficient blockchain technologies for digital art and NFTs, moving away from energy-intensive proof-of-work systems to more sustainable proof-of-stake alternatives. This shift addresses previous environmental concerns while maintaining the benefits of digital art ownership.
2. Bio-Art and Living Materials
A growing number of artists are experimenting with living materials such as mycelium, bacteria, and algae to create artworks that are not only sustainable but also biodegradable. These bio-based materials offer revolutionary approaches to sculpture and installation art, where the artwork itself becomes part of natural cycles.
3. Carbon-Neutral Studios and Exhibitions
Art studios and galleries in 2026 are implementing carbon-neutral practices, including solar power installations, LED lighting, and sustainable HVAC systems. Many institutions now calculate and offset the carbon footprint of exhibitions, setting new standards for environmental responsibility in the art world.
4. AI-Assisted Sustainable Design
Artificial intelligence tools are helping artists optimise material usage, predict the environmental impact of their projects, and discover innovative, sustainable alternatives. This technology enables artists to make more informed decisions about their creative processes while minimising waste.
Challenges and Innovations in Sustainability in Art
Adopting sustainable art practices comes with its challenges and opportunities for innovation.
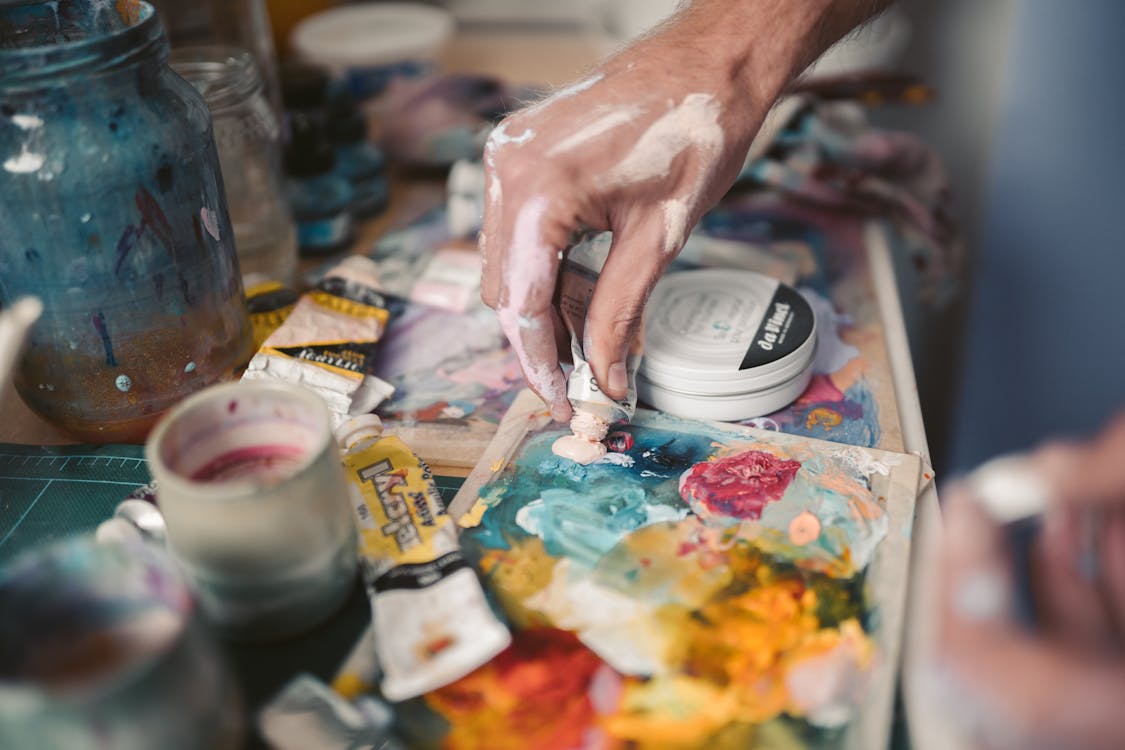

Obstacles Faced in Adopting Sustainable Art Practices
Traditional art processes often involve materials and techniques that may not align with environmentally conscious practices. Traditional pigments and solvents can be derived from non-renewable resources or contain harmful chemicals. The challenge is to find sustainable alternatives that maintain the quality and longevity of the artwork while minimising environmental impact.
Artists also encounter issues related to the availability and cost of eco-friendly materials and the need for more awareness or acceptance of these practices within the art community. This necessitates reevaluating established artistic methods and a willingness to explore innovative approaches that prioritise artistic integrity and ecological responsibility.
Innovations and Technological Advancements in Eco-Friendly Art
The art world is witnessing exciting innovations in technology and materials that are environmentally friendly. From developing biodegradable art supplies to using sustainable digital mediums, such as eco-friendly printing and 3D printing using recycled materials, artists are exploring new avenues to create art with a reduced environmental impact.

The Future of Sustainability in Art Beyond 2026
The future of sustainability in art looks promising. With growing awareness and the continuous evolution of eco-friendly materials and techniques, more artists are likely to embrace sustainable practices. As advancements in technology and innovation continue, there’s expected to be a positive trajectory towards a more sustainable art landscape. Collaborations between artists, art institutions, and environmental organisations will likely drive this change forward.
Conclusion – Sustainability in Art
Creating environmentally friendly art is essential in fostering a sustainable and responsible approach to artistic expression.
The art world continually adapts and innovates to overcome existing challenges. As the momentum towards sustainability gains strength, the future holds immense potential for a more eco-conscious art industry, paving the way for an environmentally friendly and responsible creative community. Diverse and inclusive art practices contribute to sustainable and equitable art communities, enriching the collective efforts toward long-term cultural and environmental well-being. In this dynamic landscape, artists, organisations, and initiatives collectively contribute to a narrative where artistic expression harmonises seamlessly with ecological mindfulness, promising a vibrant and sustainable creative future.

